Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of industries and manufacturing, the quest for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and minimal downtime has led to the evolution of maintenance strategies. Predictive maintenance, a proactive approach to equipment upkeep, has gained prominence in recent years.
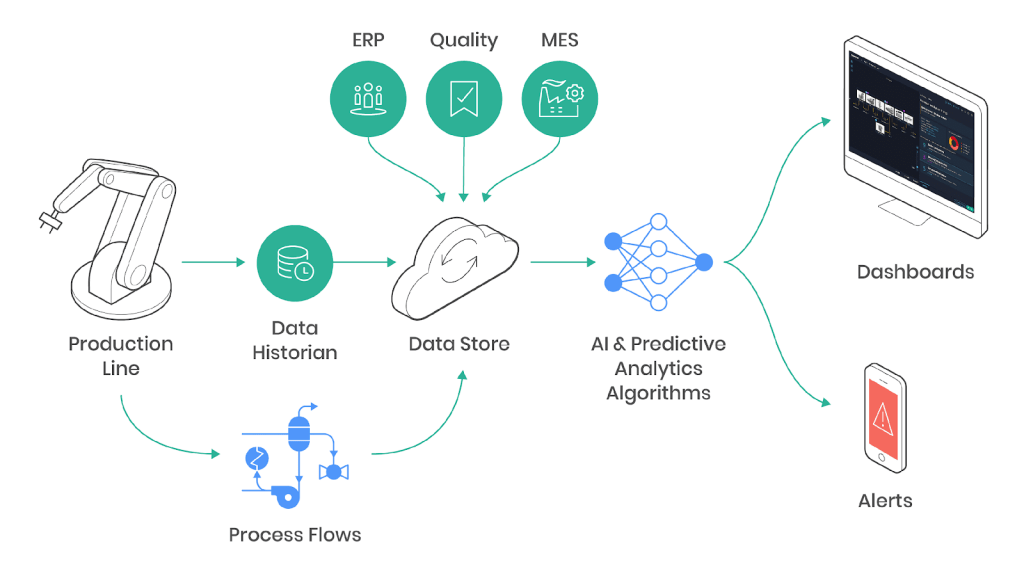
This article explores the concept of predictive maintenance with a special focus on the pivotal role of AI in predictive maintenance plays in enhancing its effectiveness.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a strategic maintenance approach that leverages data, sensors, and analytics to predict when equipment failures might occur. Unlike traditional reactive or preventive maintenance, which relies on fixed schedules or breakdowns to initiate maintenance activities, predictive maintenance anticipates issues before they escalate.
Key Components of Predictive Maintenance
- Data Acquisition: The first step in predictive maintenance involves collecting data from various sources, such as sensors, historical records, and real-time monitoring systems.
- Data Analysis: Advanced analytics processes the acquired data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential failure indicators.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: These algorithms use historical and real-time data to predict when a piece of equipment is likely to fail, allowing maintenance teams to intervene just in time.
- Condition Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of equipment conditions in real-time to detect deviations from normal functioning.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Offers actionable insights by recommending optimal maintenance actions based on predictive analysis.
The Role of AI in Predictive Maintenance
Artificial Intelligence, with its ability to analyze vast datasets at high speeds and identify complex patterns, has become a game-changer in the realm of predictive maintenance.
1. Data Processing and Analysis
AI algorithms excel at processing and analyzing massive datasets in real-time. They can discern subtle patterns and anomalies that might go unnoticed by human operators. This capability is crucial for predicting equipment failures before they occur.
2. Machine Learning for Predictive Modeling
Machine Learning (ML) algorithms, a subset of AI, are instrumental in building predictive models. These models learn from historical data to forecast equipment behavior, enabling organizations to schedule maintenance activities at the most opportune times, thus reducing downtime.
3. Continuous Improvement with Adaptive Learning
One of the strengths of AI in predictive maintenance is its ability to adapt and learn continuously. As new data becomes available, AI systems refine their predictive models, improving accuracy over time. This adaptive learning is invaluable in dynamic industrial environments where equipment and operating conditions may change.
4. Real-time Monitoring and Alerts
AI-powered systems provide real-time monitoring of equipment conditions. When deviations from normal parameters are detected, automated alerts are generated, enabling swift responses to potential issues. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of unplanned downtime.
Benefits of AI in Predictive Maintenance
The integration of AI into predictive maintenance processes brings forth a myriad of benefits for industries seeking optimal asset performance.
1. Reduced Downtime
By predicting equipment failures before they occur, AI helps organizations schedule maintenance during planned downtimes, minimizing disruptions to operations.
2. Cost Savings
Proactive maintenance strategies facilitated by AI reduce the need for costly emergency repairs and extend the lifespan of equipment. This, in turn, leads to significant cost savings over time.
3. Increased Equipment Reliability
AI algorithms can identify patterns that may indicate impending failures well in advance. This early detection enhances equipment reliability by addressing issues before they can escalate into major problems.
4. Efficient Resource Allocation
Predictive maintenance, guided by AI insights, allows organizations to allocate resources more efficiently. Maintenance teams can focus on specific equipment that truly requires attention, avoiding unnecessary interventions on well-functioning assets.
5. Improved Safety
By addressing potential equipment failures in a timely manner, AI in predictive maintenance contributes to a safer working environment. This is particularly crucial in industries where equipment malfunctions pose risks to personnel.
Challenges and Considerations
While the advantages of integrating AI into predictive maintenance are evident, there are challenges and considerations that organizations must navigate.
1. Data Quality and Integration
The effectiveness of AI models relies heavily on the quality and integration of data from various sources. Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to erroneous predictions and compromise the reliability of the entire system.
2. Initial Investment and Training
Implementing AI in predictive maintenance requires a significant initial investment in technology and training. Organizations need to ensure that their teams are adequately trained to interpret and act upon the insights provided by AI systems.
3. Security Concerns
As AI systems are increasingly connected to the internet and networks, security becomes a critical consideration. Protecting the integrity and confidentiality of the data being used for predictive maintenance is paramount.
4. Ethical Considerations
AI systems, when making decisions based on historical data, may inadvertently perpetuate biases present in that data. Ensuring ethical AI practices is essential to prevent discriminatory outcomes and maintain fairness in decision-making.
Case Studies: AI in Predictive Maintenance Success Stories
1. General Electric (GE)
GE implemented an AI-driven predictive maintenance system across its fleet of aircraft engines. By analyzing data from sensors and historical records, GE can predict engine failures with high accuracy, allowing for timely maintenance and minimizing downtime.
2. Siemens
Siemens utilizes AI to monitor and predict the performance of its industrial turbines. The system analyzes data from sensors, weather forecasts, and historical records to optimize turbine operations and schedule maintenance when necessary.
Future Trends and Developments
The landscape of AI in predictive maintenance is dynamic, with ongoing developments shaping its future.
1. Integration with IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is becoming increasingly intertwined with AI in predictive maintenance. The integration of IoT sensors allows for more comprehensive data collection, enabling AI systems to make even more accurate predictions.
2. Edge Computing for Real-time Analysis
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying on centralized servers, is gaining traction. This allows for real-time analysis of data, further reducing the time it takes to detect and respond to potential equipment failures.
3. Advancements in Explainable AI
As AI systems become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for transparency in decision-making. Advancements in Explainable AI aim to make the decision-making processes of AI systems more understandable and interpretable for human operators.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into predictive maintenance is revolutionizing how industries manage their assets. By harnessing the power of data, machine learning, and real-time analytics, organizations can move from reactive and preventive maintenance strategies to a proactive and predictive approach. The benefits, including reduced downtime, cost savings, and improved safety, make the investment in AI for predictive maintenance a strategic imperative for forward-thinking industries. As technology continues to evolve, the synergy between AI and predictive maintenance is expected to unlock new possibilities, ensuring a future where assets operate at their optimal potential.
Leave a comment