Introduction
In the fast-paced world of logistics, efficiency is key. Companies are constantly seeking innovative solutions to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance. One of the game-changing technologies in this domain is Generative AI, a powerful tool that has the potential to transform the logistics landscape. This article explores the role of Generative AI platforms in revolutionizing logistics and highlights the benefits and challenges associated with their implementation.
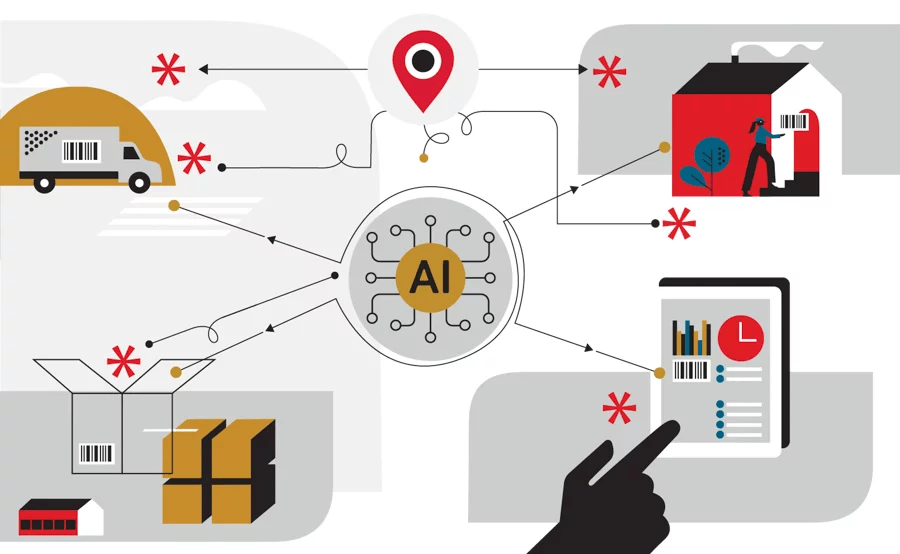
I. Understanding Generative AI
A. What is Generative AI?
Generative AI platform for logistics refers to a class of algorithms that can generate new content or data resembling that which they were trained on. Unlike traditional AI systems that rely on explicit programming, generative models learn patterns and structures from data, allowing them to create original outputs.
B. Types of Generative AI Models
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): GANs consist of two neural networks – a generator and a discriminator – competing against each other. The generator creates data, and the discriminator evaluates it. This adversarial process continues until the generator produces realistic outputs.
- VAEs (Variational Autoencoders): VAEs learn the underlying distribution of input data and generate new samples by sampling from this distribution. They are known for their ability to generate diverse and high-quality outputs.
II. Applications of Generative AI in Logistics
A. Route Optimization
Generative AI platform for logistics can analyze historical data, weather patterns, and real-time traffic information to optimize delivery routes. By continuously learning and adapting to changing conditions, these platforms can enhance the efficiency of logistics operations, reducing fuel costs and delivery times.
B. Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial in logistics. Generative AI platforms can analyze vast amounts of historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant factors to predict future demand. This enables companies to optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and reduce excess inventory.
C. Warehouse Management
Generative AI plays a vital role in optimizing warehouse operations. It can predict the optimal placement of products, automate inventory tracking, and even optimize picking and packing processes. This results in improved warehouse efficiency and reduced operational costs.
D. Predictive Maintenance
In the logistics industry, maintaining a fleet of vehicles and equipment is a significant cost factor. Generative AI platforms for logistics can predict when equipment is likely to fail by analyzing sensor data and historical maintenance records. This proactive approach to maintenance minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of assets.
III. Benefits of Implementing Generative AI in Logistics
A. Increased Efficiency
Generative AI platforms optimize various aspects of logistics operations, leading to increased efficiency. From route planning to inventory management, these systems can analyze vast datasets quickly and provide real-time insights, enabling faster and more informed decision-making.
B. Cost Reduction
By optimizing routes, minimizing idle time, and improving overall operational efficiency, generative AI platforms contribute to significant cost reductions. Companies can save on fuel expenses, labor costs, and maintenance expenditures, ultimately improving their bottom line.
C. Enhanced Customer Experience
Efficient logistics directly translate to improved customer experiences. Generative AI helps in accurate demand forecasting, reducing delivery times, and ensuring products are in stock. This leads to satisfied customers who receive their orders promptly and reliably.
D. Sustainability
Optimizing routes and reducing fuel consumption not only cut costs but also contribute to environmental sustainability. Generative AI platform for logistics aligns with the growing focus on green and sustainable practices by minimizing the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
IV. Challenges and Considerations
A. Data Privacy and Security
Generative AI relies heavily on data, and logistics companies handle sensitive information, including customer details and delivery routes. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse.
B. Implementation Costs
While the long-term benefits of generative AI in logistics are substantial, the initial implementation costs can be significant. Companies need to carefully weigh the upfront expenses against the anticipated returns on investment.
C. Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating generative AI platforms with existing logistics systems can be complex. Compatibility issues, data migration challenges, and the need for employee training are aspects that must be carefully considered during the implementation process.
D. Ethical Considerations
As with any advanced technology, ethical considerations arise. Logistics companies must ensure that the use of generative AI aligns with ethical standards, particularly when it comes to decision-making processes that may impact employees or customers.
V. Case Studies
A. Amazon
Amazon, a pioneer in logistics and e-commerce, utilizes generative AI for route optimization and warehouse management. The company’s sophisticated algorithms analyze real-time data to adjust delivery routes dynamically, ensuring timely deliveries and minimizing fuel consumption.
B. DHL
DHL, a global logistics leader, employs generative AI for demand forecasting and predictive maintenance. By accurately predicting future demand and proactively maintaining their fleet, DHL has significantly improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
VI. Future Trends and Outlook
Generative AI in logistics is an evolving field with continuous advancements. As technology progresses, we can expect further improvements in predictive capabilities, increased automation, and enhanced integration with other emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain.
VII. Conclusion
Generative AI integration is reshaping the logistics industry by optimizing operations, reducing costs, and improving overall efficiency. As companies continue to embrace these technologies, it is crucial to address challenges related to data privacy, integration, and ethical considerations. The benefits, however, far outweigh the challenges, positioning generative AI as a transformative force in the future of logistics. As we move forward, the collaboration between human expertise and generative AI innovation will pave the way for a more efficient and sustainable logistics ecosystem.
Leave a comment